The differences between a web app and a mobile app

With all the different kinds of software and the ever-evolving landscape of technical development, it is easy to get lost among the various technologies and to see the differences between them. In this article, we put a custom web application development and mobile apps in the spotlight, highlighting their characteristics, pros and cons, examples, the business models they are particularly fit for, and the programming languages that are used to create them.
What is a web application?
A web application is a software application that runs in a web browser and uses web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Unlike traditional desktop applications, web applications do not require installation or updates on individual devices and can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. A web application is not a regular website as it is designed to perform specific functions and provide a more interactive experience for the user. Unlike a regular website, which is designed to provide information, a web application is designed to allow users to interact with a website, perform specific tasks, and get results in real-time.
In what business situations does it work best?
- E-commerce: Web applications allow businesses to sell products and services online with features such as online shopping carts, product catalogs, and secure payment gateways.
- Customer Service: Web applications can be used to provide customer support, including Chatbots, knowledge bases, and support forums.
- Collaboration: Web applications can be used to facilitate collaboration among employees with features such as project management tools, document sharing, and team communication apps.
- Marketing: Web applications are used to create and manage marketing campaigns, landing pages, email marketing, and for social media management.
Example of a web application:
There are many examples of web applications, from social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter, to productivity tools like Google Docs and Trello, and e-commerce sites like Amazon and Etsy. Other examples:
- Made Trade: an ethical online shop selling anything from cookware to apparel. Made Trade is a user-friendly e-shop.
- QB Generator: QB Generator is an Exam Generator & Results Management system for Total Training Support LTD.
- Freedom United: Freedom United is the world’s largest community aiming at ending human trafficking & modern slavery.
- Prochat: A chatbot platform that enables communication with customer service. Additionally, it has features that help HR companies with the automation of recruitment processes.
What are a web app’s benefits for the business?
Web applications offer a wide range of business benefits, including:
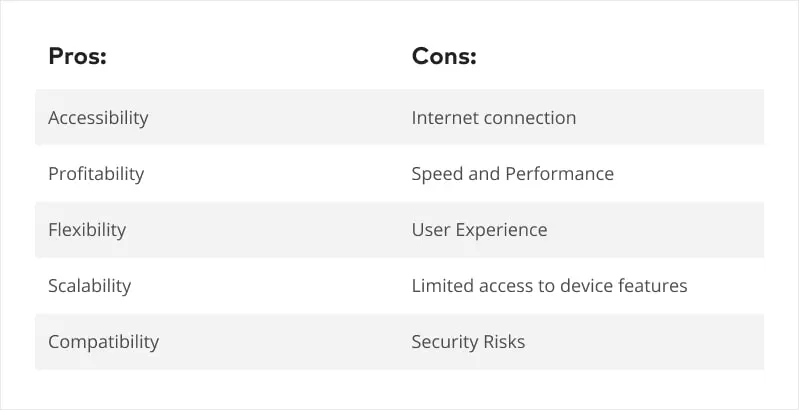
- Accessibility: Web applications can be accessed from anywhere with an Internet connection, making them ideal for businesses with remote employees, multiple offices, or customers in different locations.
- Profitability: Web applications can be more cost-effective than native mobile apps because they do not require separate development for different operating systems.
- Flexible: Web applications can be easily updated and customized, allowing businesses to adapt to changing market conditions and customer needs.
- Scalability: Web applications can scale to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes without requiring large hardware investments.
- Compatibility: Web applications are compatible with a wide range of devices and operating systems, making them accessible to a wider audience.
What are the disadvantages?
While web applications offer many advantages, they also have some disadvantages that need to be considered, including:
- Internet connection: Web applications require an internet connection to work, which can be a drawback for businesses with unreliable or slow internet connections.
- Speed and Performance: Web applications may not be as fast and efficient as native applications, especially if they require heavy data processing or complex operations.
- User Experience: The user experience of a web app may not be as seamless or intuitive as a native app, which can negatively impact user engagement and retention.
- Limited access to device features: Web applications may have limited access to device hardware and features, which may limit functionality and user experience.
- Security Risks: Web applications are vulnerable to security risks such as malware attacks and hacks, which can compromise user data and damage a business’s reputation.
What are programming languages?
- HTML, CSS and JavaScript: These are the underlying web technologies used to create the visual and interactive elements of a web application.
- PHP: PHP is a server-side scripting language commonly used for web development.
- Python: Python is a flexible programming language well-suited for web development, especially for complex and data-intensive applications.
- Ruby: Ruby is a dynamic and expressive programming language commonly used for web development with the Ruby on Rails framework.
- Java: Java is a popular programming language for web development, especially for enterprise-scale applications.
Other programming languages and frameworks used in web development include .NET, Node.js, Angular, and React. Your choice of programming language and framework depends on the specific needs and goals of your web application.
Web applications – summary
Web applications have become an integral part of modern business life. They have various advantages such as improved customer retention and satisfaction, increased brand awareness and loyalty, and increased sales and revenue. The flexibility and accessibility of web applications make them a popular choice for businesses of all sizes and industries. Note, however, that a web application is not a regular website, It requires a specific architecture that includes important parts such as user interface, a server, and databases. Understanding the differences between web and mobile apps and their strengths and weaknesses can help businesses make informed decisions about platform selection. With the right approach and strategy, web applications can help organizations achieve their goals and drive success in today’s digital age.
What is a mobile application?
Mobile applications have become an integral part of our lives. From communication to entertainment to shopping, you can perform a variety of tasks and activities on the go. In this article, we’ll look at what mobile applications are, their strengths and weaknesses, and the programming languages used to develop them. A mobile application (or simply a mobile app) is a software application designed to run on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Unlike web applications, which require a web browser to function, mobile apps can be downloaded and installed directly on mobile devices from app stores and other distribution platforms.
According to a recent report, app downloads will grow slightly from 86.7 billion to 88.3 billion in 2021. This indicates a significant increase in app downloads over the last five years, with downloads more than doubling over that period. The chart below shows quarterly app downloads in billions from 2015 to 2022.
In what business situations are they most effective?
Mobile applications can be used in a variety of business situations, including:
- E-commerce and retail: Retailers can use the app to showcase products, offer special deals, and provide seamless checkout and payment options.
- Travel and Hospitality: Mobile apps enable travelers to book flights, hotels, and rental cars, and provide maps, recommendations, and other travel-related information.
- Healthcare: Mobile apps enable patients to monitor their health, book appointments, and receive personalized treatment plans.
- Banking and Finance: Mobile apps can be used to provide secure and convenient access to bank accounts, investment portfolios, and other financial services.
Examples of Mobile Applications:
There are countless mobile apps serving different purposes in different app stores. Common examples of mobile apps are:
- Social media apps such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
- Messaging apps such as WhatsApp, iMessage, and Signal.
- Entertainment apps such as Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify.
- Gaming apps such as Candy Crush, PUBG, Among Us.
- Productivity apps like Microsoft Office, Google Drive, and Trello.
What are the benefits of mobile applications for businesses?
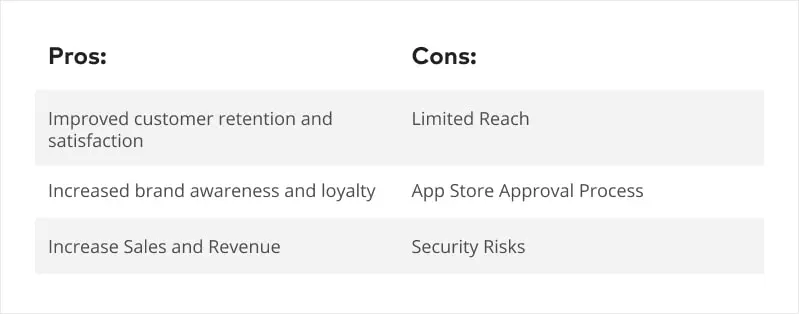
Mobile applications offer many business benefits, including increased customer retention and satisfaction, increased brand awareness and loyalty, and increased sales and revenue. By communicating directly with customers via mobile apps, businesses can provide personalized and relevant content, offers, and services. This allows you to build brand awareness and loyalty by providing a seamless and convenient user experience. Additionally, mobile apps enable businesses to generate more sales and revenue through targeted promotions and recommendations, streamlining the checkout process for a faster and more convenient shopping experience. Overall, mobile apps are valuable tools for businesses looking to connect with their customers and drive growth.
What are the disadvantages of mobile applications for businesses?
Mobile applications also have the following disadvantages:
- Limited Reach: While mobile applications can be a great tool for engaging with customers, they also have a limited reach compared to other forms of digital marketing. Not everyone has a smartphone or tablet, and not everyone downloads apps. Businesses should consider other forms of digital marketing, such as social media, email marketing, and search engine optimization, to reach a wider audience.
- App Store Approval Process: App stores have strict policies and approval processes that can delay the release of mobile apps.
- Security Risks: Mobile apps can pose security risks, especially if they require access to sensitive data such as personal or financial information.
What are the programming languages for mobile app development?
Programming languages and frameworks used to develop mobile apps include:
- Native Android: Java and Kotlin for Android app development.
- Native iOS: Swift and Objective-C for iOS app development.
- Cross platform: React Native and Flutter for cross-platform app development.
Mobile applications – summary
Mobile applications offer businesses a great opportunity to improve customer retention, increase sales and revenue, and build brand awareness and loyalty. However, developing and maintaining mobile apps can be costly and time-consuming, so businesses should carefully weigh the pros and cons before deciding to invest in mobile app development.



















